RESEARCH
PAPER ON GOLDEN SPICE IN GLOBAL MARKETS: TRENDS, CHALLENGES, AND OPPORTUNITIES
FOR INDIAN TURMERIC"
Abstract
Turmeric (“Haldi”), a staple spice
in Indian households, has gained significant global recognition for its
culinary, medicinal, and cosmetic benefits. India’s dominance in the turmeric
market, both in terms of production and export, is unrivaled. This paper
provides a comprehensive analysis of turmeric production, exports, market
trends, and emerging opportunities. Additionally, it delves into the latest
data from 2024-25, major turmeric-producing companies, their market shares,
GI-tagged turmeric varieties, and recommendations for enhancing India's
position in the global turmeric market.
1.
Introduction
Turmeric (Curcuma longa), a rhizome
belonging to the ginger family, is widely cultivated in tropical regions. Known
for its high curcumin content, turmeric is used in food, medicine, cosmetics,
and as a natural dye. India accounts for over 80% of the world’s turmeric
production and dominates the export market, catering to the rising global
demand.
1.
Global Turmeric Production
Table
1: Top 10 Haldi Producing Countries (2024-25)
|
Rank |
Country |
Estimated
Production (Million Tons) |
|
1 |
India |
8.2 |
|
2 |
China |
0.52 |
|
3 |
Thailand |
0.43 |
|
4 |
Myanmar |
0.38 |
|
5 |
Peru |
0.32 |
|
6 |
Vietnam |
0.27 |
|
7 |
Indonesia |
0.21 |
|
8 |
Bangladesh |
0.16 |
|
9 |
Nepal |
0.11 |
|
10 |
Sri Lanka |
0.09 |
India’s dominance stems from optimal
climatic conditions, fertile soil, and centuries-old cultivation practices.
States such as Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Odisha are
the primary producers.
Export
Trends and Statistical Analysis (2014–2024)
Export
Volume and Value Trends
Indian turmeric exports have shown
consistent growth in both volume and value over the last decade due to
increasing global demand for natural and organic products.
Table
2 : Indian Turmeric Export Trends (2014–2024)
|
Year |
Export
Volume (Metric Tons) |
Export
Value (USD Million) |
|
2014 |
72,000 |
123 |
|
2015 |
84,500 |
150 |
|
2016 |
98,000 |
176 |
|
2017 |
105,000 |
200 |
|
2018 |
122,000 |
240 |
|
2019 |
135,000 |
280 |
|
2020 |
145,000 |
320 |
|
2021 |
158,000 |
350 |
|
2022 |
170,000 |
390 |
|
2023 |
190,000 |
430 |
|
2024 |
210,000 |
475 |
Here is the line graph visualizing the
year-on-year trends in Indian turmeric exports (2014–2024), showcasing both
export volume (in metric tons) and export value (in USD million)
Top
Exporting Companies
Table 3 :The contribution of major companies
has been pivotal in India’s export growth.
|
Company
Name |
Export
Share (Avg.) |
Key
Destinations |
|
A.G. Agro Exports |
12% |
USA, UAE |
|
ITC Limited |
8% |
EU, Japan |
|
Patanjali Ayurved |
10% |
UAE, UK |
|
Everest Spices |
6% |
Middle East |
|
Organic India Pvt. Ltd. |
7% |
USA, Canada |
Export
Value by Region (2024)
- North America:
35%
- Europe:
25%
- Asia-Pacific:
20%
- Middle East and Africa: 15%
- Others:
5%
Statistical
Insights
- Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for turmeric export
value: 12.5% (2014–2024).
- CAGR for export volume: 10% (2014–2024).
.
Indian Turmeric Export Data (2024-25)
Table
4: Indian Turmeric Export Overview
|
Metric |
Value |
|
Total Turmeric Export Shipments |
265,000 |
|
Number of Indian Exporters |
8,100 |
|
Number of International Buyers |
28,000 |
|
Total Export Volume (Metric Tons) |
1.5 lakh |
|
Total Export Value (USD) |
475 million |
The United States, the United
Kingdom, the UAE, and Malaysia are the primary destinations for Indian turmeric
exports. The global preference for Indian turmeric is due to its superior
quality and high curcumin content.
4.
Major Turmeric Companies in India and Market Share
Table
5: Leading Indian Turmeric Exporters (2024-25)
|
Company Name |
Market Share (%) |
Key Products |
|
A.G. Agro Exports |
12% |
Whole turmeric, turmeric powder |
|
Patanjali Ayurved |
10% |
Organic turmeric |
|
ITC Limited |
8% |
Processed turmeric products |
|
Neelam Food Products Ltd |
7% |
Turmeric powder |
|
Sri Sri Tattva |
6% |
Ayurvedic turmeric products |
|
Godrej International |
5% |
Turmeric extracts |
These companies contribute
significantly to India’s dominance in the global turmeric market by offering
high-quality, competitively priced products.
5.
GI-Tagged Turmeric Varieties in India
India is home to several GI-tagged
turmeric varieties that highlight regional specialties:
- Sangli Turmeric
(Maharashtra): Renowned for its deep orange hue and high curcumin content.
- Erode Turmeric
(Tamil Nadu): Known for its bright yellow color and medicinal properties.
- Nizamabad Turmeric
(Telangana): Popular for its aromatic flavor.
- Alleppey Turmeric
(Kerala): High curcumin content, ideal for export.
6.
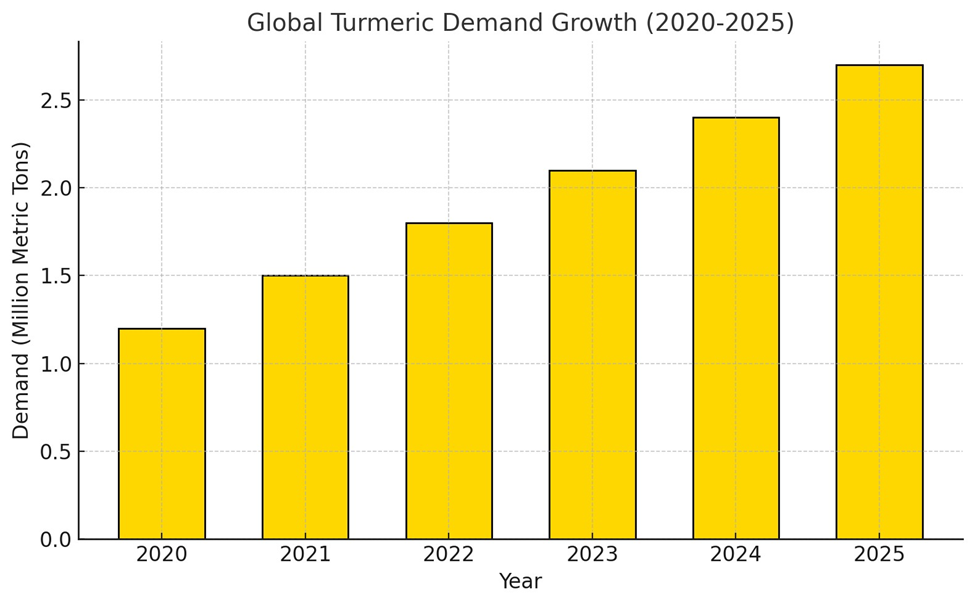
Trends in Global Turmeric Demand
The rising awareness of turmeric’s
medicinal properties, particularly its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant
benefits, is driving global demand. Organic turmeric and value-added products
like turmeric latte mixes, capsules, and essential oils are gaining traction in
international markets.
Here is the bar graph showing the steady growth of global
turmeric demand from 2020 to 2025.
7.
Challenges in Turmeric Production and Export
- Price Fluctuations:
Dependence on monsoons affects production and pricing.
- Quality Control:
Ensuring uniform curcumin levels is critical for maintaining export
standards.
- Global Competition:
Emerging players like Myanmar and Peru are intensifying competition.
- Organic Certification:
Meeting stringent organic standards for export markets.
8 Government Strategies to Boost Turmeric Products
1. Export
Promotion Policies: Provide subsidies and incentives to exporters,
particularly for value-added turmeric products.
2. Infrastructure
Development: Establish turmeric processing units, cold storage
facilities, and logistics hubs in major producing states.
3. Research
and Innovation Funding: Allocate resources for R&D in
turmeric-based nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
4. Marketing
Support: Organize international trade fairs and marketing campaigns
highlighting India’s GI-tagged turmeric varieties.
5. Farmer
Support Programs: Introduce training programs for farmers to adopt
organic and sustainable farming practices, ensuring higher yields and better
market access.
6. Digital
Platforms: Launch e-marketplaces for turmeric to connect farmers with
global buyers, ensuring transparency and better price realization.
7. Collaboration
with Ayurveda and Pharma: Promote partnerships between turmeric
farmers, Ayurveda manufacturers, and pharmaceutical companies to boost domestic
and export demand.
8. Brand
India Initiative: Create a global brand identity for Indian turmeric,
emphasizing its superior quality, medicinal benefits, and heritage.
9. Opportunities and Recommendations
1. Focus
on Value-Added Products: Indian exporters should diversify their
product portfolio to include turmeric-based nutraceuticals, cosmetics, and
functional foods.
2. Enhanced
Branding and Marketing: Highlight the uniqueness of GI-tagged
varieties to attract premium buyers.
3. Digital
Integration: Use technology to improve traceability and transparency
in the supply chain.
4. Collaborations:
Encourage partnerships between farmers and exporters for better price
realization.
5. Research
and Development: Invest in innovations to enhance productivity and
reduce post-harvest losses.
10.
Conclusion
India’s unparalleled position in the
global turmeric market provides immense opportunities for growth. By focusing
on quality, innovation, and sustainability, India can further consolidate its
dominance and achieve its export target of USD 1 billion by 2030. India’s
turmeric industry has experienced exponential growth in the last decade, driven
by increased global awareness of its health benefits. The strategic focus on
GI-tagged varieties, value-added products, and sustainable cultivation
practices can further enhance India’s dominance in this market. Achieving a
target export value of USD 1 billion by 2030 is plausible with concerted efforts
from stakeholders
11.
References
- Eximpedia.app. (2024). Haldi Export Data and Insights.
- Spice Board of India Reports (2023-24).
- Trade Data Analysis Reports (2024).
- Government of India: Ministry of Agriculture and
Farmers’ Welfare.

Comments
Post a Comment