Case Study: Allegations of Employment Discrimination at Foxconn's
iPhone Assembly Plant
Abstract
This case study examines the hiring practices at Foxconn's iPhone assembly
plant in Tamil Nadu, India, where allegations of discrimination against married
women have surfaced. The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) criticized labor
officials for failing to properly investigate these claims. This study explores
the controversy, NHRC’s intervention, similar corporate examples, and future
implications for workplace equality.
Introduction
Foxconn, a key manufacturing partner of Apple, has faced scrutiny over its
hiring practices at its iPhone assembly plant in Tamil Nadu, India. The NHRC
has criticized labor officials for failing to thoroughly investigate
allegations of discrimination against married women in assembly line jobs. This
case study explores the controversy, NHRC’s intervention, and similar corporate
examples of alleged workplace discrimination.
Background of the Case
Foxconn operates a major iPhone assembly plant in Tamil Nadu, India,
employing over 33,000 women. Reports indicate that married women were largely
excluded from assembly line jobs, a policy that was reportedly relaxed only
during peak production periods. The NHRC intervened after Tamil Nadu labor
officials submitted a report that failed to directly address allegations of
discriminatory hiring practices.
Reuters' investigation found that recruitment advertisements between January
2023 and May 2024 specified eligibility criteria limiting assembly line roles
to unmarried women within a certain age bracket. This practice contradicts
India’s Equal Remuneration Act and Apple’s and Foxconn’s own
anti-discrimination policies. Following media scrutiny, Foxconn instructed
recruiters to remove such criteria from job advertisements.
Data Analysis and Graphs
Employment Statistics
at Foxconn's Tamil Nadu Plant
|
Category |
Total Employees |
Married
Employees |
Percentage
Married |
|
Women |
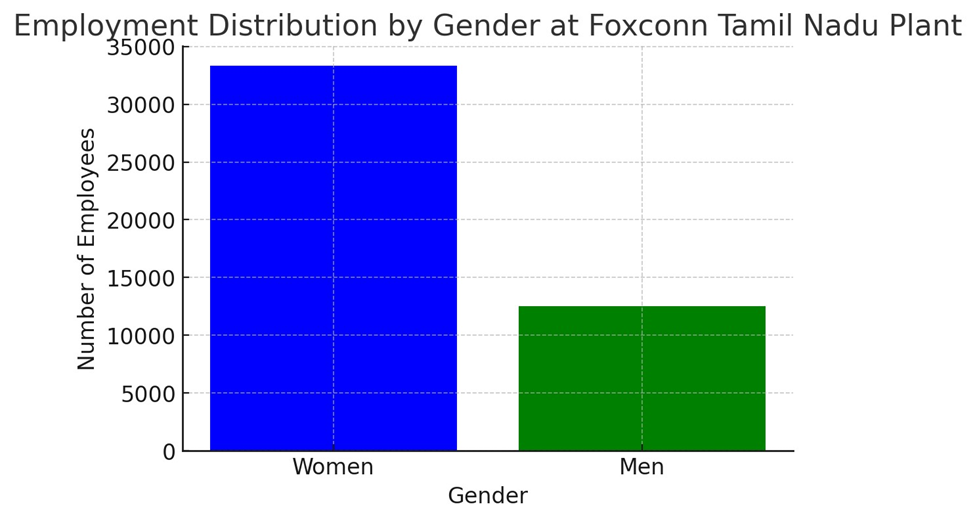
33,360 |
2,234 |
6.7% |
|
Men |
12,500 |
Data Unavailable |
- |
|
Total |
45,860 |
Data Unavailable |
- |
Graph 1: Employment Distribution by Gender (A bar chart
visualizing the employment distribution between men and women at the plant)
A bar chart displaying employment distribution by gender at Foxconn's Tamil
Nadu plant.
Graph 2: Percentage of Married Women in Workforce
A pie chart illustrating the percentage of married women in the workforce.
NHRC’s Response and Actions
The NHRC criticized labor officials for submitting a superficial report and
failing to scrutinize Foxconn’s hiring documents. The commission emphasized
that merely hiring a percentage of married women does not refute allegations of
discrimination. It ordered a thorough investigation within four weeks and
retained the authority to recommend remedial actions, including compensation
for affected workers.
Similar Corporate Examples of Workplace Discrimination
1. Samsung
and Gender Discrimination (South Korea) Samsung has faced multiple
allegations of gender discrimination, particularly regarding hiring and
promotions. In 2019, the company was fined for systemic bias against women in
recruitment processes.
2. Walmart
Gender Discrimination Case (USA) In 2001, Walmart faced a major
class-action lawsuit, Dukes v. Walmart Inc., where female employees
alleged systemic pay and promotion discrimination. Though the case was later
dismissed on procedural grounds, it raised significant awareness about gender
bias in large corporations.
3. Nike
Gender Pay Gap Lawsuit (USA) In 2018, former female employees sued
Nike for wage discrimination and creating a hostile work environment. The case
led to policy changes in pay structures and promotion transparency.
4. Tata
Consultancy Services (TCS) Age Discrimination (India) In 2015, TCS
faced accusations of laying off experienced employees in favor of younger
recruits. The controversy highlighted concerns about implicit bias in hiring
and retention policies.
Teaching Notes
1. Discussion
Questions:
o
How can companies ensure compliance with
anti-discrimination laws while maintaining operational efficiency?
o
What role should regulatory bodies like the NHRC
play in monitoring corporate hiring practices?
o
How can multinational corporations like Apple
influence their suppliers to follow ethical hiring policies?
o
Compare the Foxconn case with other global
examples of employment discrimination. What similarities and differences do you
observe?
2. Key
Takeaways:
o
The importance of transparency in recruitment
processes.
o
The role of regulatory bodies in enforcing labor
laws.
o
How multinational corporations can enforce
ethical policies across their supply chain.
Implications and Future Outlook
The Foxconn case underscores the importance of corporate accountability in
adhering to fair hiring practices. As global supply chains and multinational
corporations expand their operations in India, regulators must enforce labor
laws effectively. Transparency in recruitment processes, strict compliance with
anti-discrimination policies, and proactive labor monitoring are essential to
fostering an inclusive workforce.
Foxconn and Apple must ensure that their hiring practices align with legal
and ethical standards. Strengthening corporate governance, implementing
independent audits, and empowering labor unions could prevent similar
controversies in the future.
Conclusion
The NHRC’s intervention in the Foxconn case highlights the ongoing struggle
for workplace equality in India’s manufacturing sector. Drawing from global
corporate examples, it is evident that businesses must proactively address
discrimination to build a fair and diverse work environment. This case serves
as a critical lesson for multinational corporations operating in emerging
economies, reinforcing the necessity for ethical hiring practices and robust
labor rights enforcement.
Recent developments have shed more
light on the allegations of employment discrimination at Foxconn's iPhone
assembly plant in Tamil Nadu, India. The National Human Rights Commission
(NHRC) of India has criticized labor officials for conducting an inadequate
investigation into these claims. The NHRC found that the officials' report
lacked scrutiny of Foxconn's hiring documents and failed to address whether the
company discriminated against married women during recruitment. Consequently,
the NHRC has ordered a new, thorough investigation to be completed within four
weeks.
In response to earlier reports
highlighting discriminatory hiring practices, Foxconn has instructed its
recruitment partners in India to remove age, gender, and marital status
criteria from job advertisements for iPhone assembly workers. Additionally,
recruiters have been directed to omit Foxconn's name from these ads and to
refrain from speaking to the media. Despite these directives, it remains
unclear whether Foxconn has effectively increased the hiring of married women.
These actions follow a Reuters
investigation that revealed Foxconn had excluded married women from assembly
line jobs at its Sriperumbudur factory, a practice that was reportedly relaxed
during peak production periods. The investigation found that recruitment
advertisements between January 2023 and May 2024 specified eligibility criteria
limiting assembly line roles to unmarried women within a certain age bracket.
This practice contradicts India’s Equal Remuneration Act and both Apple’s and
Foxconn’s anti-discrimination policies.
The NHRC's intervention underscores
the importance of thorough investigations into allegations of workplace
discrimination and the need for companies to adhere strictly to
anti-discrimination laws and policies. As the situation develops, it will be
crucial to monitor the outcomes of the NHRC's mandated investigation and any
subsequent actions taken by Foxconn and its recruitment partners to ensure
compliance with ethical hiring practice
References
1. Reuters
Investigation Reports (2024-2025)
2. National
Human Rights Commission Reports
3. India’s
Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
4. Case
Studies on Walmart, Nike, Samsung, and TCS
5. Apple
and Foxconn Corporate Hiring Policies

Comments
Post a Comment