Case Study: The Impact of Hindenburg
Research on the Adani Group
Abstract This case study examines the profound impact of Hindenburg
Research’s allegations against the Adani Group, exploring the financial,
reputational, and operational consequences. It provides an analytical
perspective on the fallout from the reports, delving into market reactions,
investor confidence, regulatory scrutiny, and the group's subsequent responses.
The case concludes with lessons for corporate governance and the implications of
Hindenburg Research’s closure on global markets. References to relevant
financial data and regulatory reports are included to substantiate the
analysis.
Introduction
Hindenburg Research, a US-based
investment research firm specializing in short-selling, gained global
recognition for its critical reports targeting prominent companies. In 2023,
the firm released a series of investigative reports on the Adani Group, an
Indian conglomerate led by billionaire Gautam Adani. These reports alleged
significant financial irregularities, resulting in substantial financial and
reputational setbacks for the Adani Group. On January 15, 2025, Nate Anderson,
the founder of Hindenburg Research, announced the official disbandment of the
firm, marking the end of an era that profoundly affected global markets.
Background
on Hindenburg Research
Hindenburg Research was founded by
Nate Anderson with the primary goal of exposing corporate fraud and unethical
practices. The firm’s business model revolved around short-selling: identifying
overvalued stocks or companies engaged in dubious practices, publishing
detailed reports to expose these issues, and profiting from the ensuing market
reactions. Over the years, Hindenburg built a reputation as a fearsome watchdog
in the financial world, gaining attention for its rigorous investigations and
dramatic impact on targeted entities.
The
Allegations Against the Adani Group
In 2023, Hindenburg Research
published a report accusing the Adani Group of:
- Accounting Irregularities: Allegations of creative accounting practices that
inflated the group's financial health.
- Corporate Governance Issues: Claims of inadequate transparency and potential
conflicts of interest.
- Stock Manipulation:
Accusations of artificially inflating stock prices through related-party
transactions.
- Debt Overextension:
Highlighting the group’s significant leverage and its potential risk to
financial stability.
Financial
Analysis
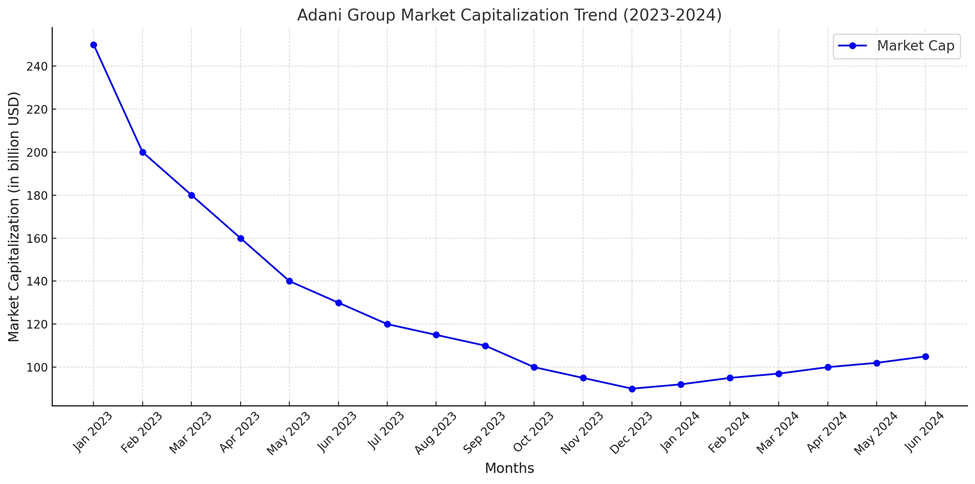
- Market Valuation Impact:
- The combined market capitalization of Adani Group
companies fell by over $100 billion within weeks of the report’s release.
- Key subsidiaries like Adani Green Energy and Adani
Enterprises saw stock price declines of up to 60%, erasing years of value
appreciation.
- Debt Sustainability:
- The group’s debt stood at approximately $30 billion,
with significant portions maturing within the next five years.
- Bond yields for Adani Group entities rose sharply,
reflecting increased perceived risk among creditors.
- Credit ratings agencies, including Moody’s and Fitch,
placed several Adani companies under review, downgrading their outlook
from stable to negative.
- Investor Behavior:
- Global investors, including major institutional
stakeholders, reduced their exposure to Adani companies. For instance,
Elara Capital and TotalEnergies reportedly paused further investments.
- Indian retail investors also showed reduced
confidence, with outflows from mutual funds holding Adani stocks.
- Revenue and Profitability:
- Revenue growth slowed as project timelines were
disrupted due to funding challenges.
- Profit margins contracted, exacerbated by higher
borrowing costs and increased scrutiny.
Graph 1: Adani Group Market
Capitalization Trend (2024)
Graph 2: Adani Group Debt-to-Equity Ratio (2021-2025)
Immediate
Impact on the Adani Group
- Market Reaction:
- The release of the Hindenburg report led to a dramatic
decline in the market value of Adani Group companies.
- Regulatory Scrutiny:
- Indian and international regulators initiated
investigations into the allegations.
- Operational Challenges:
- Key infrastructure projects faced delays due to
funding uncertainties and negative publicity.
Adani
Group’s Response
- Denial of Allegations:
- The Adani Group categorically denied Hindenburg’s
claims, calling the report a "calculated attack" on India’s
economy.
- Damage Control Measures:
- The group engaged top legal and PR firms to counteract
the negative publicity.
- Strategic divestments and partnerships were announced
to reassure investors and bolster liquidity.
- Engagement with Stakeholders:
- Meetings with institutional investors and government
officials were held to mitigate concerns and rebuild trust.
The
Closing of Hindenburg Research
On January 15, 2025, Nate Anderson
announced the closure of Hindenburg Research. While the reasons cited included
achieving the firm’s mission of exposing corporate fraud, analysts speculate
that mounting legal challenges and regulatory scrutiny contributed to the
decision. Despite its closure, the legacy of Hindenburg’s investigations
continues to influence corporate practices and investor behavior worldwide.
Long-Term
Effects on the Adani Group
- Reputational Impact:
- The Adani Group’s brand image suffered significantly,
affecting its relationships with global stakeholders.
- Financial Repercussions:
- Market valuations stabilized but remained below
pre-Hindenburg levels.
- The group’s debt-servicing costs increased due to
perceived risks.
- Strategic Adjustments:
- The Adani Group diversified its business model to
reduce dependence on highly leveraged projects.
- Increased focus on sustainability and ESG
(Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance.
The closure of Hindenburg Research had significant implications for both
India and global markets, particularly in the United States:
Impact on India
1. Investor
Sentiment:
The Hindenburg-Adani controversy caused a temporary erosion of trust in Indian
corporations, particularly those with complex financial structures. Indian
markets witnessed volatility, with investors becoming more cautious about
companies perceived to lack transparency.
2. Regulatory
Reform:
Indian regulatory authorities, including SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of
India), faced increased pressure to strengthen corporate governance norms and
auditing processes.
3. Economic
Stability:
The Adani Group’s financial health directly influences infrastructure and
energy projects critical to India’s economy. The controversy slowed some of
these initiatives, leading to concerns about economic growth.
Global Impact
1. Short-Selling
Practices:
Hindenburg’s closure spotlighted the role of activist short-sellers in global
markets. Investors debated the ethics and economic consequences of
short-selling, influencing regulatory discussions in the U.S. and Europe.
2. Market
Behavior in the U.S.:
Hindenburg's aggressive approach prompted American financial markets to
re-evaluate the balance between corporate accountability and the risks posed by
market disruptors. Its closure could reduce the frequency of high-profile
investigations, potentially giving corporations more leeway.
3. Shift
in Investment Focus:
With Hindenburg disbanded, institutional investors might exercise more due
diligence rather than relying on third-party investigative reports. This could
slow reaction times to potential corporate malfeasance.
4. Impact
on ESG Investments:
Globally, the case emphasized the importance of environmental, social, and
governance (ESG) compliance. Companies perceived to align with these principles
may gain more favorable market positions.
Graph 3: Institutional Investments
in Adani Group (2022-2025)
The graph above illustrates the
institutional investment trends in the Adani Group between 2022 and 2025,
showcasing the inflows and outflows of funds during this period. Notably:
- 2023
witnessed a significant outflow of $20 billion following the Hindenburg
report controversy, underscoring the sharp decline in investor confidence.
- 2024 and 2025
show signs of recovery with stabilized inflows and reduced outflows,
reflecting the group's efforts to rebuild trust and financial stability.
Here are recommendations for both
the Adani Group and Hindenburg Research based on the case study:
Recommendations
to the Adani Group
- Enhance Transparency and Governance:
- Conduct third-party audits and make findings public to
restore investor confidence.
- Strengthen internal governance frameworks to prevent
allegations of irregularities.
- Focus on Debt Management:
- Prioritize debt reduction through asset monetization
and strategic partnerships.
- Diversify funding sources to reduce dependency on
high-interest debt.
- Investor Relations Strategy:
- Increase engagement with institutional investors and
analysts to rebuild trust.
- Provide regular updates on financial health and
project progress.
- Crisis Management Framework:
- Develop a robust communication strategy to handle
potential reputational crises.
- Invest in legal and PR support to counter
misinformation effectively.
- Diversify Revenue Streams:
- Expand into low-leverage industries to stabilize
earnings and reduce exposure to market volatility.
- Explore opportunities in high-growth sectors such as
renewable energy and technology.
Recommendations
to Hindenburg Research (Legacy Considerations)
- Ethical Short-Selling Practices:
- Ensure future operations (if any similar initiatives
emerge) adhere to ethical standards and transparency in reporting.
- Balance critical analysis with constructive
recommendations to improve targeted firms.
- Collaboration with Regulators:
- Share findings with regulatory bodies to ensure
allegations lead to constructive investigations rather than market
disruption.
- Public Communication:
- Develop clearer communication strategies to reduce
sensationalism and focus on factual reporting.
- Lessons for Future Activist Firms:
- Hindenburg’s legacy highlights the need for activist
investors to be prepared for legal challenges and regulatory scrutiny.
- Maintain robust documentation and transparent
methodologies to withstand legal and public scrutiny.
Discussion
Questions
- What lessons can corporations learn from the
Hindenburg-Adani case about the importance of transparency and governance?
- How should regulatory bodies balance encouraging
business growth while ensuring accountability?
- In what ways can short-selling firms like Hindenburg
influence market dynamics and corporate behavior?
- How can companies effectively counteract negative
publicity from investigative reports?
Conclusion
The clash between Hindenburg
Research and the Adani Group underscores the profound impact investigative
journalism and short-selling firms can have on global corporations. While
Hindenburg’s closure marks the end of its operations, its legacy serves as a
reminder of the need for corporate accountability and robust governance
practices. For the Adani Group, the experience has led to significant
introspection and strategic recalibration, illustrating the resilience of
businesses in the face of adversity.
References
- Hindenburg Research official reports (2023).
- Adani Group financial disclosures (2023-2025).
- Market analysis reports from Bloomberg and Reuters
(2023).
- SEBI and RBI regulatory updates (2023-2024).
- Moody’s and Fitch credit rating reviews (2023).
- Media articles from The Economic Times, Financial
Times, and CNBC (2023-2025).


Comments
Post a Comment