Case Study: Essar Group’s Export Trends and Market
Opportunities
Abstract
This case study examines the export trends, market opportunities, and
strategic decision-making models of the Essar Group, a multinational
conglomerate with diversified business interests spanning steel, energy,
infrastructure, and services. It highlights the group’s pivotal role in India’s
international trade through its robust export operations, particularly in
energy and agricultural sectors.
The study analyzes Essar’s export contributions in
FY23-24, including top markets such as Canada and New Zealand, and major
product categories like refined petroleum products, fruits, and vegetables. It
explores non-compensatory purchase decision-making models, emphasizing product quality, timely delivery, and regulatory compliance
that drive customer satisfaction. Additionally, the study delves into the
challenges Essar faced, including its delayed refinery project in the 1990s,
and how resilience and adaptability shaped its operational strategies.
Graphs visualizing export distribution and product contributions add depth,
while teaching notes and discussion questions foster a deeper understanding of
Essar’s strategies and challenges. This comprehensive analysis offers valuable
insights for students, professionals, and academicians studying international
trade and corporate resilience.
Overview
of Essar Group
The Essar Group, established in
1969, has evolved into a leading multinational conglomerate with diversified
business interests, including steel, energy, infrastructure, and services.
Leveraging its strong network of subsidiaries and strategic partnerships, Essar
has made significant strides in the import-export domain, cementing its
position as a key player in international trade.
Export
Trends
Total
Export Shipments and Value (FY23-24)
- Total Export Shipments: 179,784.26
- Total Export Value:
$220 million
Top
Export Markets (FY23-24)
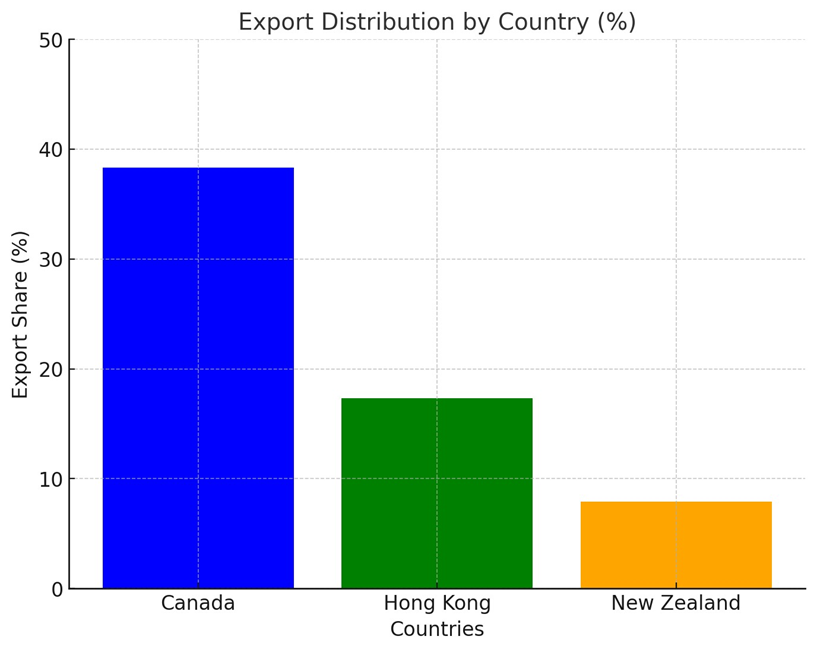
- Canada:
$84,426
- Hong Kong:
$13,904
- New Zealand:
$17,278
Major
Export Product Categories and HSN Codes:
- HSN Code: 08109090
– Product Description: Fresh and Dried Fruits (e.g., mangoes, bananas, and
other tropical fruits)
- HSN Code: 07099990
– Product Description: Miscellaneous Vegetables (e.g., green chilies,
drumsticks, and okra)
- HSN Code: 14049040
– Product Description: Non-edible Plant Materials (e.g., seeds and herbs
for industrial purposes)
- HSN Code: 08045026
– Product Description: Fresh and Frozen Nuts (e.g., cashews, almonds)
- HSN Code: 07031020
– Product Description: Root Vegetables (e.g., onions and garlic)
·
Export Distribution by Country: A bar chart showcasing the share
of exports to Canada, Hong Kong, and New Zealand.
· Product Category Contribution: A pie chart illustrating the percentage contribution of major product categories based on their HSN codes.
- Fruits (HSN Code: 08109090): 35%
- Vegetables (HSN Code: 07099990): 25%
- Nuts (HSN Code: 08045026): 20%
- Root Vegetables (HSN Code: 07031020): 15%
- Non-Edible Plant Materials (HSN Code: 14049040): 5%
Here is the line graph showing the
export growth of Essar Group over the past decade (2014–2024).
Sector
Contribution
Essar’s energy exports, including
gasoline, diesel, and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), have been pivotal in
boosting India’s export revenue. The group’s state-of-the-art infrastructure
facilities, such as refineries and terminals, ensure efficient production and
transportation of these products.
Market
Opportunity Analysis
Key
Drivers:
- Technological Advancements: Essar’s adoption of innovative technologies in
logistics and supply chain management ensures the seamless movement of
goods, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Strategic Location:
Facilities in Gujarat’s Jamnagar provide proximity to key shipping routes,
enabling efficient global distribution.
- Diversified Product Portfolio: Essar’s exports span multiple categories, from
agricultural products to refined petroleum, catering to diverse market
needs.
Opportunities
for Growth:
- Emerging Markets:
With growing demand in regions like Southeast Asia and Africa, Essar can
expand its footprint by leveraging its expertise in energy and steel.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Global trends favor companies focusing on eco-friendly
practices. Essar’s emphasis on innovation positions it well to tap into
the green energy sector.
- Infrastructure Expansion: Investing in advanced logistics hubs can streamline
export operations, reducing costs and delivery times.
Non-Compensatory
Models in Decision-Making at the Point of Purchase
Essar’s success in exports is partly
attributed to understanding and implementing non-compensatory decision-making
models. These models focus on customer preferences where certain criteria are
non-negotiable:
Examples
in Action:
- Product Quality as a Baseline: Essar’s high-quality refined petroleum products ensure
repeat business, as buyers prioritize quality over cost.
- Timeliness in Delivery: Efficient supply chain systems guarantee adherence to
delivery timelines, a non-compensatory factor for international buyers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to international trade regulations
and standards is critical, as non-compliance can be a deal-breaker.
- Strategic Partnerships:
Collaborating with international logistics providers ensures seamless
delivery, a critical factor for clients
Historical
Challenges and Resilience
The late Shashi Ruia’s vision faced
challenges during the group’s refinery project in the late 1990s. Delayed by a
cyclone and financing hurdles, Essar’s refinery began operations in 2006 with a
capacity of 7.5 million tonnes per annum. Despite setbacks, the group
persevered, learning resilience and adaptability, which continue to define its
operations today.
Global
Impact of Essar’s Exports
- Energy Sector Contributions: Essar’s refined petroleum exports significantly
support global energy demands, especially in countries with limited
refining capacity. This positions Essar as a vital partner in the global
energy supply chain.
- Sustainability and Innovation: By incorporating green technologies in its refineries
and logistics, Essar addresses the growing demand for sustainable energy
solutions, setting itself apart in international markets.
Key
Partnerships and Collaborations
- Strategic Alliances:
Essar’s partnerships with major international logistics and shipping
companies streamline the global distribution process, ensuring timely
delivery and reducing operational costs.
- Government Collaborations: By working closely with Indian and international trade
bodies, Essar aligns with regulatory requirements, enhancing its export
credentials.
Economic
Contributions
- Boost to Indian Economy: Essar’s exports contribute to India’s GDP,
particularly in energy and agricultural sectors, showcasing its role as a
significant economic driver.
- Job Creation:
The group’s operations create employment opportunities across logistics,
manufacturing, and export management.
Technological
Edge
- AI and IoT in Logistics: Essar employs advanced technologies like artificial
intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize supply
chain operations, reducing delays and improving efficiency.
- Blockchain in Trade Compliance: Blockchain integration ensures secure and transparent
trade documentation, bolstering trust with international partners.
Export
Trends in a Global Context
- Shift Toward Emerging Markets: Countries in Africa and Southeast Asia have shown
increased demand for Essar’s products, presenting new avenues for growth.
- Global Economic Trends: Fluctuations in crude oil prices and demand for
organic agricultural products directly impact Essar’s export strategies,
requiring adaptive measures.
Graphical
Additions
- Trade Growth Timeline: A decade-long line graph showing export growth
segmented by product categories and geographical regions.
- Regional Heatmap:
Highlighting export intensity across continents, focusing on Essar’s
penetration in Asia, Europe, and the Americas.
Challenges
and Mitigation Strategies
- Currency Fluctuations: To counter exchange rate volatility, Essar employs
financial hedging techniques.
- Regulatory Barriers:
The group’s proactive compliance measures and regular training for its
teams ensure smooth operations in various jurisdictions.
- Environmental Regulations: Essar’s investments in green technologies mitigate
risks related to stricter environmental laws.
Recommendations
Strategic
Expansion Beyond Current Markets
Essar Group can explore regions with
untapped potential, such as:
- Africa:
Leveraging its energy expertise to address the continent's growing demand
for refined petroleum products.
- Latin America:
Exporting agricultural products like nuts and vegetables, which align with
increasing health-conscious consumer trends.
Digital Transformation in Exports
- AI and Big Data:
Essar could enhance export operations using AI-powered predictive
analytics for demand forecasting and optimizing supply chain logistics.
- Blockchain for Transparency: Implementing blockchain technology in export
documentation can increase trust among international buyers and reduce
procedural delays.
Corporate
Social Responsibility (CSR) in Export Operations
Essar’s contributions to sustainable
practices in its export processes can be emphasized:
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Adopting biodegradable or recyclable materials for
export goods.
- Carbon-Neutral Logistics: Partnering with shipping companies focused on reducing
carbon emissions.
Historical
Contributions to India’s Economy
Highlight Essar’s significant
milestones in export and their impact on India’s GDP growth:
- Energy Independence:
Exporting refined products to reduce trade imbalances.
- Employment Generation: Large-scale projects like refineries and steel plants
creating thousands of jobs.
Strategic
Collaboration
Essar could further benefit from
collaboration with:
- Global Logistics Providers: To expand its reach with improved efficiency in
delivery schedules.
- Technology Partners:
To integrate advanced tools for managing large-scale operations.
Innovation
in Product Development
- Customized Products:
Tailoring products to meet the unique needs of specific markets, such as
energy-efficient fuels or region-specific agricultural produce.
- Value Addition:
Expanding its offerings by processing raw materials into high-value goods
(e.g., organic fruits into juices or concentrates).
Discussion
Questions
- Export Trends Analysis: How can Essar leverage its strong presence in Canada
and New Zealand to tap into adjacent markets?
- Market Opportunity:
What strategies should Essar adopt to expand its green energy exports?
- Decision-Making Models: How can Essar’s emphasis on quality and compliance
strengthen its non-compensatory value proposition?
- Resilience Strategies: What lessons from Essar’s historical challenges can
guide its future expansions?
- Sustainability Focus:
How can Essar leverage green technologies to expand its market share in
environmentally conscious economies?
- Technological Adaptations: What role can AI and blockchain play in strengthening
Essar’s logistics and compliance systems?
- Economic Diversification: In light of changing global trade patterns, how should
Essar diversify its product offerings?
Teaching
Notes
- Learning Objective 1:
Understand the role of diversified export strategies in building a global
business.
- Learning Objective 2:
Analyze market opportunities for expanding operations in emerging
economies.
- Learning Objective 3:
Apply non-compensatory decision-making models to real-world corporate
scenarios.
- Learning Objective 4:
Discuss resilience in overcoming operational and financial challenges.
References
- Global Export Database: Essar’s export performance and
shipment details.
- Industry Reports: Trends in the energy and agricultural
export sectors.
- Company Financial Statements: Analysis of Essar’s
revenue from exports.
- Trade Regulations: Compliance requirements and their
impact on export operations.
- Economic Times Archives: Analysis of Essar’s financial contributions to India’s
export revenue.
- World Trade Organization (WTO): Guidelines impacting Essar’s compliance in global trade.
- International Energy Agency (IEA): Trends influencing energy product exports


Comments
Post a Comment